
Have you ever paused in the personal care aisle, deodorant in hand, and wondered: “Is aluminum in deodorant bad for you?” If so, you’re not alone. The presence of aluminum in deodorant and antiperspirant products has sparked a heated debate, leading to a mix of concern, confusion, and conflicting information among consumers. With so many opinions swirling—some warning of potential health risks and others assuring safety—it’s easy to feel overwhelmed or unsure about what’s best for your body.
Let’s break it down: Why is aluminum in deodorant even a topic of controversy? Aluminum-based compounds are widely used in antiperspirants, but not in deodorants. This distinction is crucial, yet often misunderstood. While deodorants target odor by controlling bacteria, antiperspirants use aluminum salts to block sweat—two very different functions. Still, both products often get lumped together, muddying the conversation about their safety and effectiveness.
What’s fueling the concern? Over the years, questions have surfaced about whether aluminum in antiperspirants could be linked to serious health issues, such as breast cancer or Alzheimer’s disease. Some studies have suggested possible associations, while others—and many health experts—have found little or no evidence to support these fears. The result? Ongoing debate and a growing market for aluminum-free alternatives.
In this guide, we’ll tackle the core questions you may be asking:
Our goal is simple: to provide an evidence-based, balanced overview that empowers you to make informed decisions about your daily routine. Whether you’re looking to understand the science, weigh risks, or just want peace of mind, you’ll find answers here—without the hype or confusion. Ready to get clarity on aluminum in deodorant? Let’s dive in.
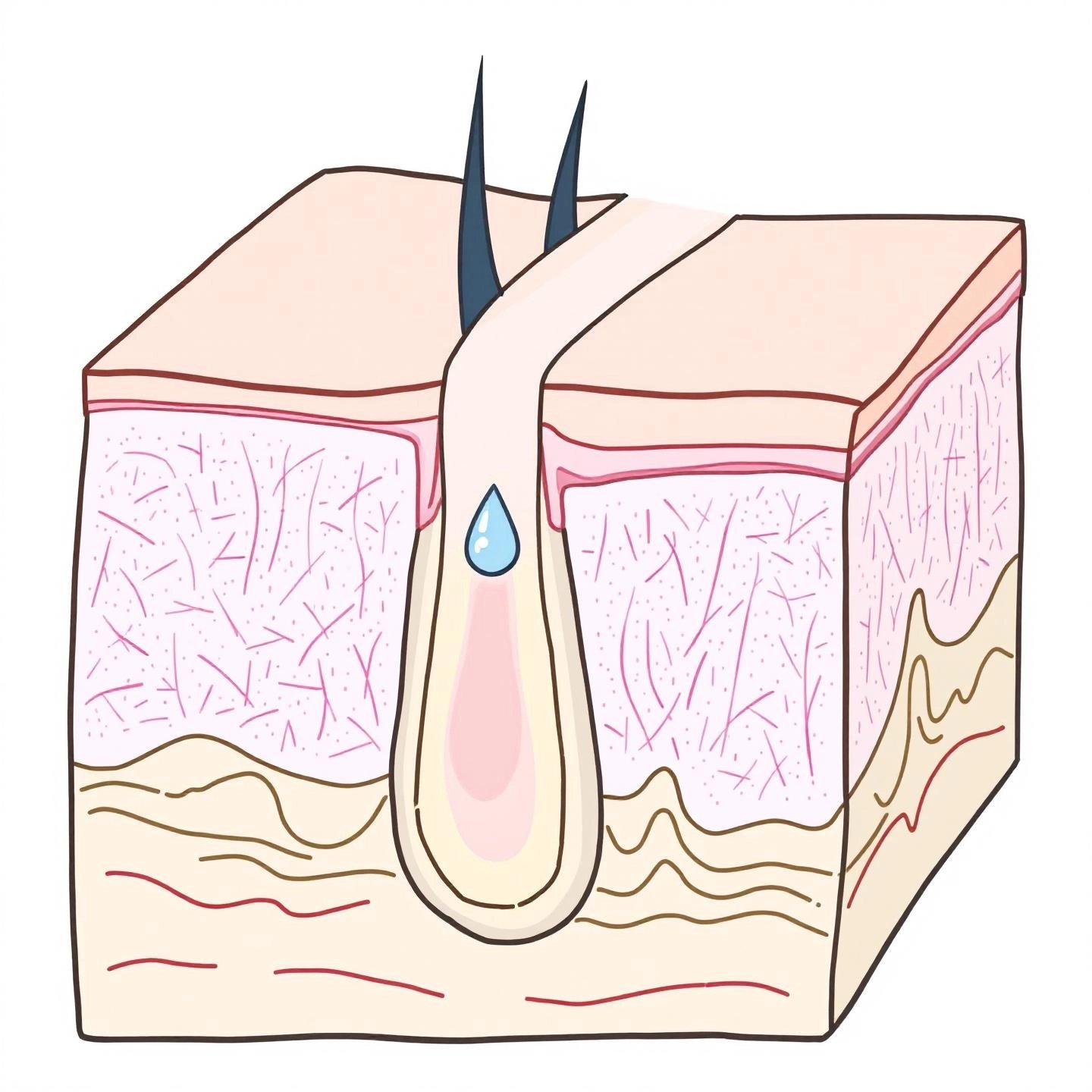
Ever wondered how antiperspirants keep you dry, even on a sweltering day or before a big meeting? The secret lies in the chemistry of aluminum-based compounds. But how does aluminum in antiperspirant work, and what exactly happens when you swipe it on your skin?
When you apply an antiperspirant, you’re not just masking odor—you’re actively reducing sweat. Here’s how it works:
This process has been confirmed by both laboratory and microfluidic experiments, showing that the plug forms within minutes of application and densifies over the course of about 30 minutes, effectively reducing sweat flow through the duct (Nature).
Not all aluminum compounds are created equal. The types of aluminum in deodorant—more accurately, in antiperspirants—determine how well the product works and how likely it is to cause irritation. Here are the most frequently used forms:
Imagine the sweat duct as a tiny tunnel. Aluminum salts dissolve, travel into the duct, and—by forming a gel with sweat proteins—create a physical barrier. This barrier isn’t permanent, but it’s strong enough to keep you dry for hours. The effectiveness depends on factors like the specific aluminum compound, the concentration, your sweat pH, and even the rate at which you sweat.
It’s also worth noting that not all aluminum salts are equally effective. For example, potassium alum—a natural mineral sometimes marketed as an alternative—does not create the same plug and has much lower clinical efficacy as an antiperspirant.
Understanding the unique action of aluminum in antiperspirants sets the stage for our next discussion: how these products differ from deodorants, and why knowing the distinction matters for your daily routine.
Ever stood in the aisle, staring at a wall of products, and wondered: "Deodorant vs antiperspirant—what’s the difference?" If so, you’re not alone. These terms are often used interchangeably, but they serve distinct purposes and are regulated differently. Let’s break down what really separates these two daily essentials, so you can make a choice that fits your needs and your comfort level with ingredients like aluminum.
Imagine you’re gearing up for a big day—maybe an important meeting or a workout. You want to feel fresh and confident. Here’s where the difference comes in:
Here’s the key: Only antiperspirants contain aluminum compounds. These are the ingredients responsible for temporarily plugging sweat ducts and reducing perspiration. In contrast, deodorants are aluminum free—they focus solely on odor, not sweat control. This distinction is important for anyone specifically seeking aluminum free deodorant options, whether for personal preference or concerns about potential health effects.
Another crucial difference is how these products are viewed by health authorities:
| Feature | Deodorant | Antiperspirant |
|---|---|---|
| Main Function | Neutralizes or masks odor | Reduces sweat and controls odor |
| Active Ingredients | Antimicrobial agents, fragrances | Aluminum compounds (e.g., aluminum chlorohydrate), plus deodorizing agents |
| Contains Aluminum? | No | Yes |
| Mechanism | Kills odor-causing bacteria; adds scent | Blocks sweat ducts to reduce perspiration |
| Regulation | Cosmetic (less strict) | OTC drug (FDA regulated) |
So, which should you choose? If your main concern is body odor and you don’t mind sweating, a deodorant—especially an aluminum free deodorant—might be all you need. If you want to minimize both sweat and odor, look for an antiperspirant. Many products combine both functions, but reading the label will help you find exactly what you’re looking for.
Understanding these differences makes it easier to match your product to your lifestyle and preferences. Next, we’ll address the big question on many minds: Are there real health risks associated with aluminum in antiperspirants, or is the concern overblown?
When you hear warnings about aluminum in deodorant, you might immediately wonder: Is aluminum in deodorant bad for you? This question is at the heart of ongoing debates, online forums, and even Reddit threads filled with personal anecdotes and concern. But what does the science actually say? Let’s break down the core worries, look at what really happens when you use an antiperspirant, and see how major health organizations weigh in on the issue.
The main worry is that aluminum-based compounds in antiperspirants could be absorbed through the skin, enter your bloodstream, and potentially cause systemic health issues—ranging from breast cancer to kidney problems and even neurological diseases. This concern is amplified by the fact that antiperspirants are applied to the underarm, an area often shaved and with thinner skin, which might, in theory, increase absorption.
Common questions include:
Sounds complex? Here’s the simple truth: Rigorous scientific studies have measured how much aluminum from antiperspirants actually gets through your skin. In a state-of-the-art clinical study using a special isotope of aluminum, researchers found that only a tiny fraction—between 0.002% and 0.06%—of the applied aluminum is absorbed through the skin, with the average being about 0.0094% (PMC6226111). To put that in perspective, the amount absorbed from daily antiperspirant use is far less than what you typically ingest from food and drinking water.
Given the low absorption rates, major health authorities have carefully reviewed the evidence:
Key takeaway: For healthy adults, the evidence overwhelmingly suggests that the use of aluminum-based antiperspirants is safe. The minute amount absorbed does not accumulate to harmful levels, and regulatory agencies continue to monitor new research to ensure ongoing safety.
Still, if you have specific health conditions—such as advanced kidney disease—it’s wise to consult your doctor before using products with aluminum. For most people, however, concerns about systemic health risks are not supported by current scientific evidence.
Now that we’ve covered the big-picture safety question, let’s look more closely at possible local side effects or other drawbacks of using aluminum-based antiperspirants—and how these compare to aluminum-free options.
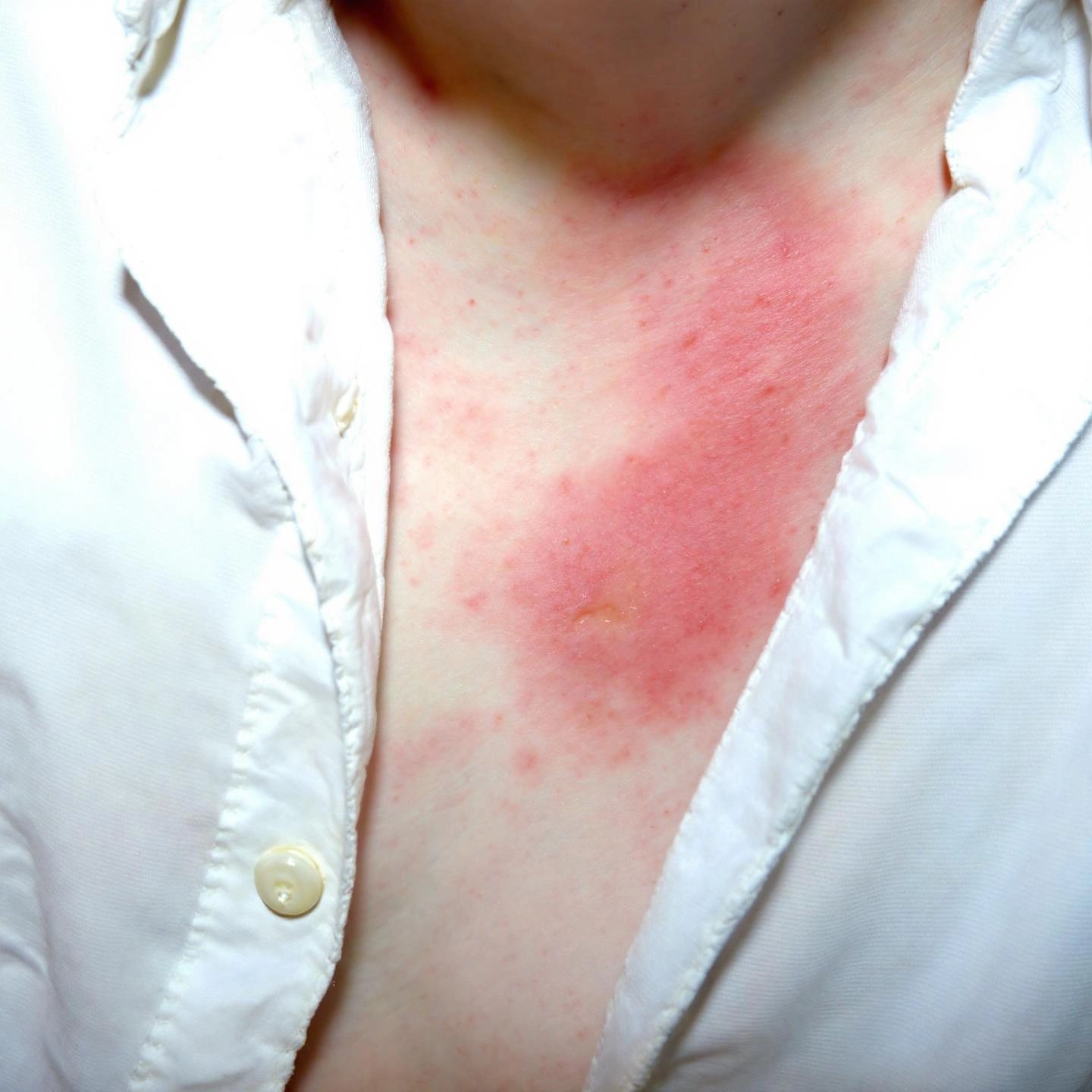
Ever wondered why your favorite white shirt ends up with yellow stains, or why your underarms sometimes feel itchy after using an antiperspirant? If so, you’re not alone. Let’s dive into the real-world aluminum in deodorant side effects—from skin reactions to the dreaded wardrobe mishaps—and see how the science stacks up against everyday experience.
When you apply an antiperspirant, you expect dryness and freshness. But sometimes, your skin may have a different reaction. Here are the most reported localized side effects:
Imagine applying your antiperspirant after a close shave—your skin is extra sensitive, and the aluminum salts can sting or cause redness. That’s why experts recommend applying these products only to intact, dry skin and preferably before bedtime, when sweating is minimal and absorption is most effective.
Ever pulled a white shirt from the laundry only to discover stubborn yellow stains under the arms? It’s not your sweat alone that causes this. The culprit is a chemical reaction between aluminum salts in your antiperspirant and the proteins in your sweat—particularly from apocrine glands in your underarms. This reaction creates yellow deposits that cling to fabrics, especially cotton, and can be tough to remove.
With side effects and stains in mind, you may wonder: Is switching to an aluminum-free deodorant the answer? Let’s weigh the options:
| Aluminum-Based Antiperspirant | Aluminum-Free Deodorant | |
|---|---|---|
| Effectiveness | Blocks sweat and odor; proven for heavy sweaters | Neutralizes odor only; does not prevent sweating |
| Side Effects | May cause irritation, redness, or cysts; can stain clothing | Lower risk of stains and irritation; less likely to block pores |
| Wardrobe Impact | Yellow stains possible on light fabrics | No yellow stains; safer for white shirts |
| Regulation | FDA-regulated as an OTC drug | Classified as a cosmetic |
Not all antiperspirants are created equal. The specific aluminum compound used, its concentration, and even the product format (spray, stick, roll-on) can influence both performance and side effects. Achieving the right balance—maximum sweat protection with minimal irritation—requires precise formulation, much like the exacting standards in industrial aluminum manufacturing. For example, Shengxin Aluminum’s meticulous approach to alloy composition and quality control in their production lines mirrors the need for precision in personal care products to ensure safety and effectiveness.
In summary, while most side effects of aluminum in deodorant are mild and manageable, knowing how these products interact with your skin and clothing can help you make smarter choices. Next, we’ll dig deeper into the most discussed health concern: the alleged link between aluminum in antiperspirants and cancer risk.
When you hear about aluminum in deodorant cancer risk, it’s natural to feel concerned—after all, breast cancer is a serious issue that touches many lives. But does aluminum in deodorant cause cancer, or is this a myth fueled by misunderstanding? Let’s unpack the science, step by step, to separate fact from fear.
The theory that antiperspirants might contribute to breast cancer began circulating because these products are applied near the breast and contain aluminum-based compounds. Some researchers speculated that aluminum could be absorbed through the skin, especially after shaving, and might interact with estrogen receptors in breast cells. Since estrogen can promote the growth of some breast cancers, this idea gained traction and led to widespread concern.
Sounds complex? Here’s what scientists have found so far:
Both the National Cancer Institute (NCI) and the American Cancer Society (ACS) have reviewed the evidence and agree: There is no convincing or consistent scientific proof that antiperspirants or deodorants increase breast cancer risk. While the hypothesis has been tested, the overall consensus is that there’s no need to worry based on current research.
Key takeaway: Despite ongoing debate, the best available science does not support a link between aluminum in deodorant and cancer. If you’re concerned, talk to your healthcare provider—but rest assured that mainstream health authorities consider these products safe for the general population.
Curious about other health concerns tied to aluminum, like Alzheimer’s disease? Up next, we’ll explore what research says about that connection and whether it’s something you need to worry about.

Ever wondered, does aluminum in deodorant cause Alzheimer's? If you’ve heard this claim, you’re not alone—concerns about a possible link have been circulating for decades, sparking confusion and anxiety for many. Let’s break down where this idea comes from, what the latest research shows, and what major health organizations—including the NHS and Alzheimer’s experts—say about the real risks.
Imagine you’re in the 1960s: researchers inject rabbits with large amounts of aluminum directly into their brains. The result? The rabbits develop brain changes—specifically, protein tangles—that looked a bit like those seen in Alzheimer’s disease. Around the same time, some studies found higher levels of aluminum in the brains of people who had died with Alzheimer’s. These findings led to speculation that everyday exposure to aluminum—from cookware, water, and yes, antiperspirants—could be a hidden culprit behind the disease.
Sounds suspicious, right? But here’s the key: just because two things happen together doesn’t mean one causes the other. The early research used doses of aluminum far higher than you’d ever get from daily life, and the brain changes in animals weren’t identical to those in human Alzheimer’s. More importantly, when someone develops Alzheimer’s, their brain’s protective barriers can break down—allowing substances like aluminum to enter and accumulate. This means higher aluminum levels in the brain could be a result of the disease, not the cause (Alzheimer's Research UK).
Over the years, researchers have looked at people with high aluminum exposure (such as those with kidney failure or rare cases of metal poisoning) and compared their rates of Alzheimer’s disease to the general population. The result? No convincing evidence that higher aluminum exposure increases Alzheimer’s risk. Even studies that found more aluminum in the brains of people with Alzheimer’s couldn’t prove that it was the cause—only that it was present.
The Alzheimer’s Association and leading UK organizations agree: there is not enough high-quality evidence to conclude that typical, everyday exposure to aluminum—including from deodorants—causes Alzheimer’s disease. In fact, most scientists now believe that any aluminum found in the brains of people with Alzheimer’s is more likely a consequence of the disease’s progression, not the trigger.
Key takeaway: Decades of research have not established a causal link between aluminum in deodorant and Alzheimer’s disease. Correlation does not mean causation, and everyday exposure is considered safe for the general population.
So, while it’s natural to wonder about the safety of ingredients in your daily routine, the current scientific consensus—supported by organizations like the NHS and Alzheimer’s Society UK—is that aluminum in deodorant is not a confirmed risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease. Next, we’ll look at what current research says about the overall safety of aluminum in antiperspirants, so you can feel confident in your choices.
When you stand in front of the bathroom mirror, applying your daily antiperspirant, you might wonder: Is aluminum in deodorant safe? With so much information—and misinformation—circulating, it’s important to break down what the latest scientific research and regulatory agencies actually say about this common ingredient.
Let’s start with the basics. Antiperspirants use aluminum-based compounds to block sweat, but does this mean your body absorbs large amounts of aluminum? The answer, according to multiple studies, is a clear no. Research shows that only a tiny fraction of aluminum applied to the skin is actually absorbed—estimates range from as little as 0.01% to 0.06% (Healthline). Most of the aluminum stays at the surface, forming a plug in the sweat duct, and is eventually washed away or shed with dead skin cells.
For a compound to cause systemic harm, it would need to be absorbed in significant amounts. The evidence shows this simply doesn’t happen with antiperspirant use.
Wondering about the official stance? The FDA on aluminum in antiperspirant is clear: these products are considered safe and effective for the vast majority of users. In fact, the FDA regulates antiperspirants as over-the-counter (OTC) drugs, requiring rigorous safety and efficacy testing before they reach store shelves (Health.com). Their main concern is for individuals with advanced kidney disease, which is why you’ll see a warning on antiperspirant labels advising those with kidney problems to consult a doctor first.
Beyond the FDA, organizations like the National Kidney Foundation and the American Cancer Society have also reviewed the evidence and found no reason for the general population to avoid aluminum-containing antiperspirants.
| Topic | Scientific Consensus | Regulatory Position |
|---|---|---|
| Skin Absorption | Extremely low (0.01–0.06%) | Not a concern for healthy individuals |
| General Safety | No evidence of harm from typical use | Considered safe and effective (FDA) |
| Special Populations | Possible risk if severe kidney disease | Warning for kidney disease patients |
| Long-Term Health Risks | No proven link to cancer or Alzheimer’s | Monitored, but no restrictions for general use |
For most people, the answer is simple: aluminum in antiperspirant is safe when used as directed. Major health authorities and scientific reviews consistently find no evidence of harm for the general population. However, if you have severe kidney disease or a specific sensitivity, talk to your doctor before use.
Understanding the science and regulations can help you make confident, informed choices. Next, let’s look at how to read product labels and weigh the benefits and drawbacks of aluminum-free alternatives—so you can decide what’s right for your routine.

Ever stood in the personal care aisle, scanning rows of products and wondering, “How do I choose the right deodorant for me?” With so many options—sprays, sticks, gels, and creams—plus the ongoing debate about aluminum in deodorant, it’s easy to feel overwhelmed. Let’s break down the process, step by step, so you can confidently select a product that matches your needs, values, and lifestyle.
Sounds complex? It doesn’t have to be. When you pick up a deodorant or antiperspirant, the first thing you’ll notice is the ingredients label. Here’s how to spot aluminum and other key components:
Choosing between an antiperspirant and an aluminum-free deodorant isn’t just about ingredients; it’s about your personal priorities. Here’s a quick comparison to help you decide:
| Antiperspirant (Contains Aluminum) | Aluminum-Free Deodorant | |
|---|---|---|
| Main Benefit | Blocks sweat and controls odor—ideal for staying dry | Neutralizes odor but allows natural sweating |
| Drawbacks | May cause skin irritation or yellow stains on clothing | Does not prevent sweating; may require frequent reapplication |
| Best For | People who want maximum dryness and odor control | Those with sensitive skin, allergies to aluminum, or seeking a more natural product |
| Cost | Generally more affordable | Often more expensive; may need to try several brands to find a good fit |
| 1. | Decide if sweat control or odor control is your top priority. |
| 2. | Read the ingredient list for aluminum compounds if you want to avoid or include them. |
| 3. | Check for potential skin irritants if you have sensitive skin. |
| 4. | Consider your budget and willingness to experiment with different products. |
| 5. | Think about your lifestyle values—organic, cruelty-free, or fragrance-free options. |
Just as choosing the right deodorant requires attention to detail and quality, so does high-performance aluminum manufacturing. For instance, Shengxin Aluminum’s advanced production capabilities and rigorous quality controls ensure consistent, reliable products for critical applications—from eco-friendly construction to high-tech transportation. Whether in your daily routine or industrial projects, precision and informed choices make all the difference.
Armed with a clear understanding of product labels and the real-world aluminum free deodorant benefits, you’re ready to make a choice that fits your needs. Next, we’ll wrap up with a summary of the key findings and an empowering message to help you move forward with confidence.
When you pause in the personal care aisle, deodorant in hand, it’s easy to feel overwhelmed by the ongoing debate about aluminum in deodorant risks. Should you worry about cancer, Alzheimer’s, or kidney disease? Or is this all just confusion and hype? Let’s recap what the evidence really shows and how you can confidently make the best choice for your daily routine.
Imagine standing in front of the mirror, knowing that your decision is grounded in science—not fear. The aluminum in deodorant reality is that, for most people, these products are safe and effective when used as directed. If you value staying dry, antiperspirants deliver proven results. If you prefer a more natural approach or want to minimize potential irritants, aluminum-free options are widely available and increasingly effective.
Just as precision and quality matter in your personal care choices, they are equally vital in the world of industrial manufacturing. Companies like Shengxin Aluminum set the standard for excellence with advanced production capabilities and a commitment to material science, ensuring reliability and safety in every application. Whether you’re choosing a deodorant or sourcing materials for a major project, attention to detail and informed decisions make all the difference.
Key takeaway: The best choice is the one that fits your lifestyle, values, and comfort—made with confidence and clarity, not confusion. Trust the science, read your labels, and know that you’re in control of your daily routine.
Thank you for joining us on this journey to uncover the real facts about aluminum in deodorant. Stay informed, stay empowered, and make every choice count.
For most healthy adults, aluminum in antiperspirants is considered safe. Scientific studies show that only a tiny amount of aluminum is absorbed through the skin, and leading health organizations like the FDA and American Cancer Society have found no evidence linking typical use to cancer or other major health risks. Those with severe kidney disease should consult a doctor before using aluminum-based products.
Aluminum-free deodorants are a good choice if you want to avoid potential skin irritation, yellow stains on clothing, or simply prefer a more natural product. However, they do not prevent sweating—only odor—so if dryness is your main priority, an antiperspirant with aluminum may be more effective. Ultimately, the decision depends on your skin sensitivity, lifestyle, and personal values.
Aluminum is not found in deodorants—only in antiperspirants. Some consumers prefer aluminum-free products due to concerns about health risks or because they want to avoid sweat duct blockage and potential side effects like skin irritation or staining. As a result, many brands now offer aluminum-free deodorant options to meet these preferences.
Research shows that only a very small percentage of aluminum from antiperspirants is absorbed through the skin—far less than what is typically ingested from food and water. The skin acts as an effective barrier, and the amount absorbed is considered negligible for healthy individuals.
Deodorants target odor by neutralizing bacteria and adding fragrance, while antiperspirants use aluminum compounds to block sweat glands and reduce perspiration. Deodorants are classified as cosmetics, whereas antiperspirants are regulated as over-the-counter drugs due to their effect on bodily functions.
 Servicio en línea
Servicio en línea 0086 136 3563 2360
0086 136 3563 2360 sales@sxalu.com
sales@sxalu.com +86 136 3563 2360
+86 136 3563 2360