Aluminum alloy extrusion is a transformative manufacturing process that shapes aluminum alloys into specific cross-sectional profiles. This technique is pivotal across various industries, including construction, automotive, and aerospace, due to its versatility and efficiency. The process begins with heating an aluminum billet to a malleable state before forcing it through a die to form the desired profile. This method allows for the creation of complex shapes, whether solid, hollow, or semi-hollow, providing significant design flexibility.
Why is aluminum alloy extrusion so significant? The answer lies in the inherent properties of aluminum alloys. These materials are lightweight yet strong, offering a high strength-to-weight ratio that is crucial for applications where weight reduction is a priority, such as in the aerospace and automotive sectors. Additionally, aluminum's natural corrosion resistance and excellent thermal and electrical conductivity make it an ideal choice for a wide range of products.
One of the standout benefits of aluminum extrusion is its sustainability. Aluminum is fully recyclable, and the extrusion process itself is energy-efficient, contributing to a lower environmental footprint. Moreover, the ability to extrude aluminum into intricate shapes with minimal tooling costs and quick production times makes it an attractive option for manufacturers looking to innovate and bring products to market swiftly.
In summary, aluminum alloy extrusion is not just a manufacturing process; it's a gateway to innovation. It combines the unique properties of aluminum with a versatile shaping technique, enabling industries to produce high-quality, durable, and sustainable products efficiently. As we delve deeper into the specifics of the extrusion process and its applications, the advantages of utilizing aluminum alloys will become even more apparent.
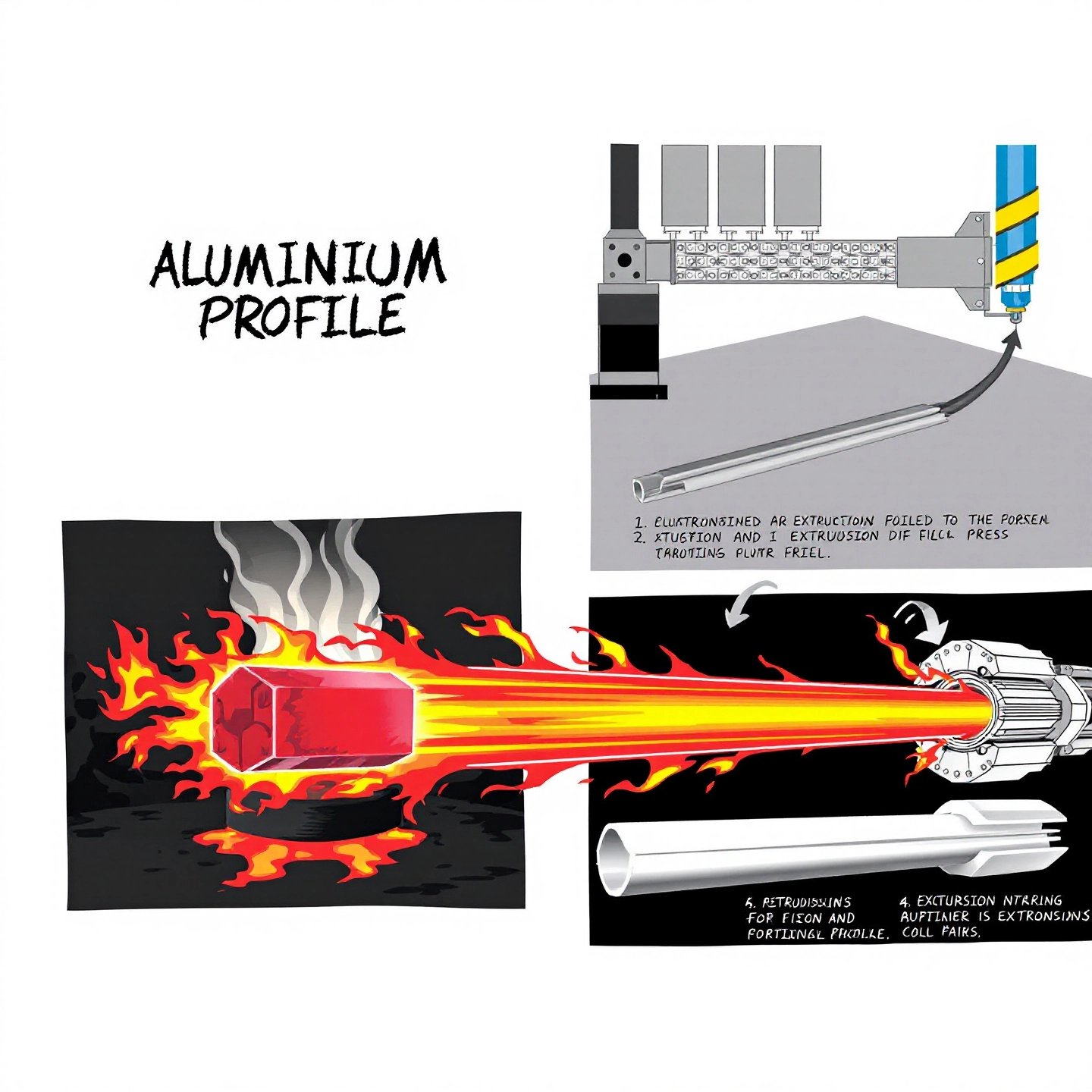
Understanding the aluminum extrusion process is crucial for appreciating the versatility and efficiency of this manufacturing technique. Here's a step-by-step breakdown of the aluminum extrusion process, highlighting each phase from start to finish:
Now, let's compare the two primary extrusion methods: direct and indirect extrusion. Each method has distinct characteristics and applications:
| Aspect | Direct Extrusion | Indirect Extrusion |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Involves pushing the billet through a stationary die using a ram. | Involves moving the container and billet together while the die remains stationary. |
| Friction | Higher friction due to billet movement, leading to more heat generation. | Lower friction, allowing better temperature control. |
| Applications | Commonly used for complex shapes and larger profiles. | Ideal for producing consistent quality in smaller, precise profiles. |
| Advantages | Versatile with a wide range of shape possibilities. | Improved surface finish and mechanical properties due to consistent temperature. |
Each method offers unique benefits, making the choice between direct and indirect extrusion dependent on the specific requirements of the project. As we move forward, understanding these nuances will be essential in selecting the right extrusion process to meet your manufacturing needs.
When it comes to aluminum alloy extrusion, selecting the right alloy is crucial for achieving desired performance and product specifications. Among the most commonly used alloys are 6061, 6063, and 6005, each offering unique properties that make them suitable for different applications. Let's delve into what makes these alloys stand out and how they impact the extrusion process.
The 6061 aluminum alloy is revered for its versatility and is often referred to as "structural aluminum" due to its excellent mechanical properties. Developed in 1935, it remains a favorite for structural applications. Here are some key characteristics:
The choice of 6061 is often driven by its balance of strength and workability, which is ideal for products requiring a robust yet easily manufacturable material.
Known as "architectural aluminum," the 6063 alloy is the most popular for extrusion due to its excellent finish and corrosion resistance. Here are its notable features:
6063's ability to be formed into intricate shapes with a smooth finish makes it a preferred choice for aesthetic applications.
The 6005 alloy offers a blend of properties that make it suitable for applications requiring moderate strength and good corrosion resistance:
Choosing the right alloy significantly impacts the extrusion process and the performance of the final product. Each alloy's unique properties determine its suitability for specific applications, ensuring that the end product meets both functional and aesthetic requirements. As we explore further, understanding these alloy characteristics will be essential in optimizing the extrusion process for your specific needs.
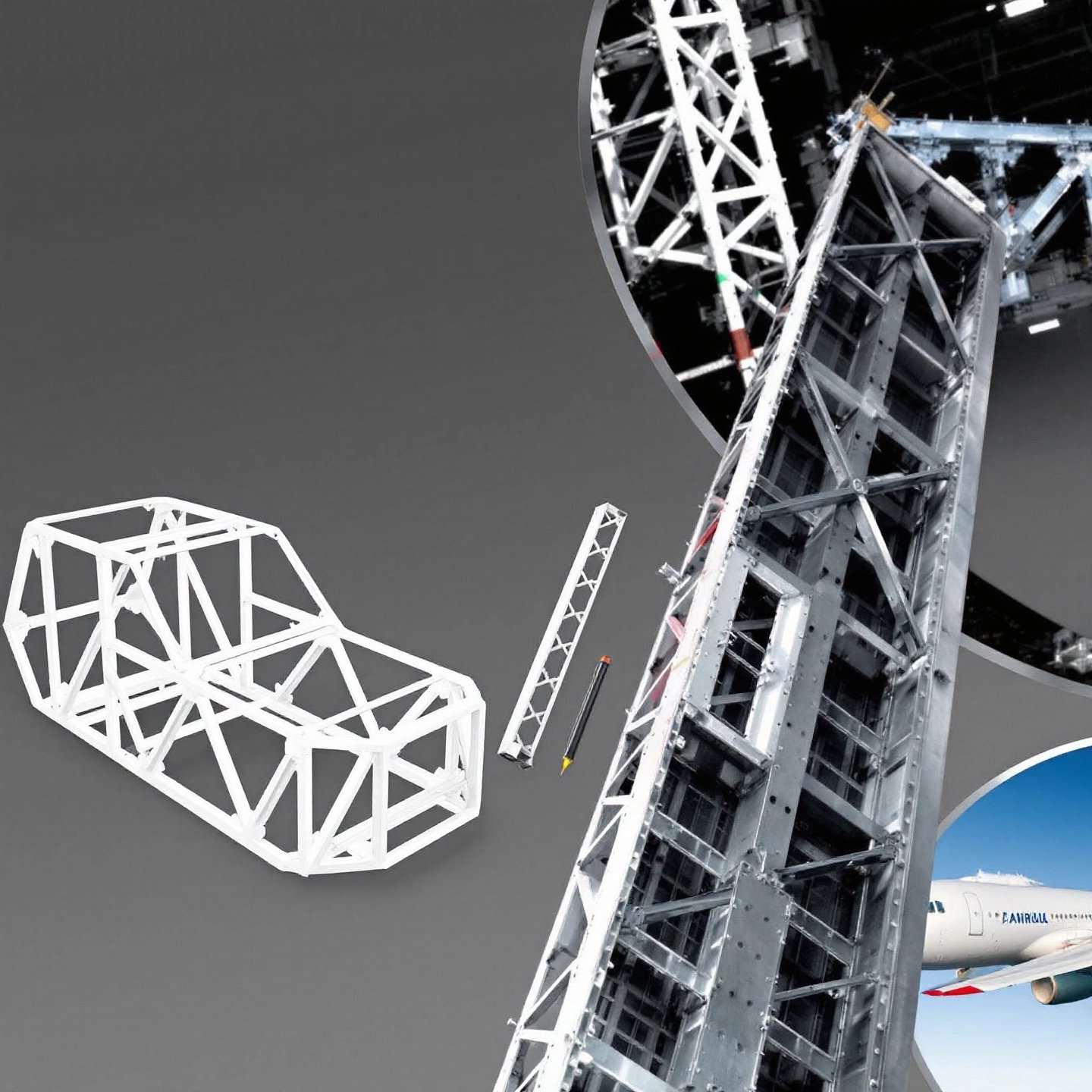

Aluminum alloy extrusions are integral to numerous industries, providing solutions that are both versatile and efficient. Let's delve into some of the key sectors where these extrusions play a pivotal role, highlighting specific products and their benefits.
In the construction industry, aluminum extrusions are indispensable. They are used in curtain walls, window frames, and roofing systems, offering a combination of strength and lightweight properties. The ability to withstand harsh weather conditions without corroding makes them ideal for outdoor applications. Aluminum's flexibility allows architects to design complex geometries, enhancing the aesthetic appeal of buildings. For instance, large skylights and canopies often rely on extruded aluminum for their structural integrity and visual elegance.
As the automotive industry seeks to improve fuel efficiency, aluminum extrusions have become increasingly essential. They are used in manufacturing vehicle frames, engine blocks, and body panels, reducing overall weight without compromising strength. This weight reduction not only boosts fuel efficiency but also enhances vehicle performance and safety. Extruded aluminum's natural corrosion resistance extends the lifespan of automotive components, making it a preferred choice for manufacturers looking to innovate in vehicle design.
The aerospace industry benefits significantly from aluminum extrusions due to their high strength-to-weight ratio. Components such as fuselage frames, seat tracks, and landing gear are commonly made from extruded aluminum, contributing to the aircraft's lightweight structure and fuel efficiency. The material's ability to withstand extreme temperatures and pressures further cements its role in aerospace engineering.
For more detailed insights on extruding 2024 aluminum alloys specifically for aerospace applications, see the Comprehensive Guide to the 2024 Aluminum Alloy Extrusion Process.
Aluminum extrusions find their way into everyday products, enhancing both functionality and design. From bicycles and camping gear to electronics and kitchen appliances, extruded aluminum offers durability and a sleek finish. Its thermal conductivity makes it ideal for heat sinks in electronic devices, ensuring efficient heat dissipation. The adaptability of aluminum allows for innovative designs in consumer products, meeting both aesthetic and practical needs.
In conclusion, aluminum alloy extrusions are a cornerstone in various industries, providing unmatched benefits in terms of strength, weight, and corrosion resistance. Their versatility enables manufacturers to create products that are not only functional but also sustainable and visually appealing. As industries continue to evolve, the demand for aluminum extrusions is set to grow, driving further innovation and application diversity.
Designing products for aluminum extrusion involves a nuanced understanding of both material properties and manufacturing capabilities. The design phase is crucial as it directly impacts the efficiency of the extrusion process and the performance of the final product. Here, we delve into key considerations and guidelines that can help optimize your aluminum extrusion design.
Effective aluminum extrusion design is a collaborative effort. Engaging with extrusion specialists early in the design process can provide insights into material behavior and manufacturing capabilities, ensuring that your design is both innovative and practical. By following these guidelines, you can enhance the quality and performance of your extruded aluminum products, setting the stage for successful applications across various industries.
When you think about aluminum products, the first thing that might come to mind is their sleek, shiny appearance. But did you know that the surface finishing of extruded aluminum is not just about looks? It's also about enhancing durability and functionality. Let's explore some of the most common surface finishing techniques used in aluminum alloy extrusion, including anodizing, powder coating, and painting.
Anodizing is a popular surface treatment for aluminum that significantly enhances its properties. This electrochemical process thickens the natural oxide layer on aluminum, improving its corrosion resistance and durability. Imagine a protective shield that not only guards against environmental damage but also offers aesthetic flexibility with vibrant colors.
Powder coating is another popular method for finishing aluminum surfaces. This technique involves applying a dry powder to the aluminum, which is then cured under heat to form a skin-like layer. The result? A durable, colorful finish that can withstand various environmental conditions.
While not as durable as anodizing or powder coating, painting remains a viable option for aluminum finishing, particularly for projects requiring specific color matches or minor touch-ups.
Surface finishing not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of aluminum products but also extends their lifespan by protecting them from environmental damage. Whether through anodizing, powder coating, or painting, choosing the right finish can significantly impact the performance and longevity of aluminum alloy extrusions. As we move forward, understanding these techniques will help you make informed decisions for your projects, ensuring both beauty and resilience in your aluminum products.
In the world of manufacturing, ensuring the quality of aluminum alloy extrusions is crucial. Quality control in the extrusion process not only guarantees the integrity of the final products but also enhances customer satisfaction and reliability. Let's explore how quality assurance is implemented throughout the extrusion process and the common defects that manufacturers aim to prevent.
Effective quality control begins with rigorous inspection methods and adherence to industry standards. These practices ensure that each extrusion meets predefined criteria for dimensional accuracy, material uniformity, and performance standards. The following are key aspects of extrusion quality control:
Despite stringent quality control measures, defects can still occur during the extrusion process. Understanding these defects and their causes is essential for implementing effective solutions:
By addressing these common issues, manufacturers can optimize the extrusion process, ensuring high-quality outcomes and enhancing product reliability.
Quality assurance in aluminum alloy extrusion is a comprehensive approach that combines meticulous inspection, adherence to standards, and the use of advanced technologies. This ensures that the final products not only meet but exceed customer expectations, contributing to their satisfaction and the overall success of the manufacturing process. As we continue exploring innovations in aluminum extrusion, maintaining high-quality standards remains a cornerstone of industry advancement.

Aluminum extrusion is not just about shaping metal; it's about shaping the future. As industries demand more efficient, sustainable, and versatile materials, aluminum extrusion is undergoing significant transformations. Let's delve into the latest advancements and trends that are setting the stage for the future of aluminum extrusion.
The integration of cutting-edge technologies is revolutionizing the aluminum extrusion process:
Advancements in aluminum alloys are expanding the possibilities of extrusion applications:
Sustainability is a driving force in the evolution of aluminum extrusion:
As these innovations continue to evolve, the future of aluminum extrusion looks promising, with potential growth areas in lightweight transportation solutions and renewable energy infrastructure. Embracing these advancements will ensure that aluminum extrusion remains an integral part of modern manufacturing, meeting the challenges of a rapidly changing world.
As we've explored throughout this article, aluminum alloy extrusion is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, offering a multitude of benefits and applications across diverse industries. From the construction of architectural marvels to the lightweight components in automotive and aerospace sectors, the versatility and efficiency of aluminum extrusions are unparalleled.
One of the key benefits of aluminum extrusion is its ability to combine strength with lightweight properties, making it an ideal choice for applications where reducing weight is crucial without compromising structural integrity. This strength-to-weight ratio, coupled with aluminum's natural corrosion resistance, positions aluminum extrusions as a sustainable and durable option for manufacturers.
The wide range of applications—from consumer electronics to renewable energy frameworks—demonstrates the adaptability of aluminum extrusions. As industries continue to seek innovative solutions that meet both performance and environmental standards, aluminum extrusions are poised to play a significant role in future advancements.
For those considering aluminum alloy extrusion for their manufacturing needs, partnering with reputable manufacturers like Shengxin Aluminum can provide access to high-quality products and expert guidance. Shengxin Aluminum, with its extensive production capabilities and commitment to quality, stands out as a leader in the field, offering tailored solutions to meet specific industry demands.
In conclusion, aluminum alloy extrusion not only meets the current needs of various industries but also holds promise for future innovations and sustainability efforts. As we embrace these opportunities, the potential for aluminum extrusions to transform manufacturing landscapes remains vast and exciting. Whether you are looking to enhance product performance or explore new design possibilities, aluminum extrusion offers a path forward that is both efficient and environmentally conscious.
Extruded aluminum alloy is formed by pushing aluminum through a die to create specific profiles. This process enhances the material's properties, making it ideal for various applications, including construction and automotive industries.
Alloy 6063 is often preferred for its excellent finish and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for architectural applications. For structural components, 6061 is favored due to its strength and versatility.
Yes, 6061 T6 aluminum is commonly extruded, particularly in the aerospace industry, where its high strength-to-weight ratio is beneficial for aircraft structures like wings and fuselage sections.
Aluminum billets are typically heated to 400-480°C (750-900°F) before extrusion, allowing the material to become malleable without losing its structural integrity.
Surface finishing techniques like anodizing and powder coating enhance durability and aesthetics by improving corrosion resistance and offering various color options for extruded aluminum products.
 Servicio en línea
Servicio en línea 0086 136 3563 2360
0086 136 3563 2360 sales@sxalu.com
sales@sxalu.com +86 136 3563 2360
+86 136 3563 2360